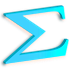Vertebrate Brain
In animal body the brain is an organ that is present in the head(close to the sensory organs) and works as the central-neural system in all vertebrate and invertebrate. The brain is the most complex organ , in a human body, the cerebral cortex is made of almost 14–16 billion neurons, and the number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Neurons are connected with each other by Synapses, and they communicate with each-other by long protoplasmic fibers called axons, which are made of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body to send or catch signals.
Basic structure of a vertebrate brain:-
- A fully formed adult brain is surrounded by meninges.
- Brain first makes its appearance in the form of 3 primary brain vesicles, Prosencephalon, Mesencephalon, and Rhombencephalon.
- The primary brain vesicle soon differentiate to form 5 major subdivisions of the adult brain-Telencephalon and diencephalon( Prosencephalon), Mesencephalon and Metencephalon(Mesencephalon), and Myelencephalon (Rhombencephalon).
Telencephalon:-
- The typical craniet telencephalon consist of paired right and left cerebral hemespere each containing a ventricle within it (1st and 2nd ventricle/lateral ventricle).
- These hemispheres are collectively are known as the cerebrain.
- Extending forward from each hemispheres is an olfactory tract and bulb.
- At the boundary between the diencephalon and telencephalon the thin embryonic neurocoel invaginates dorsally to form a wrinkled thin walled sacked , the paraphyces.
- Each ventricle present in the cerebral hemispheres is continues with the 3rd ventricle via and inter ventricular foramen. The foramen of monroe.
- Each hemispheres is divided into 2 principle chords the corpus striatum and the cortex or pallium. Corpus striatum is ventral, while the roof and side walls are formed by the cortex.
- The corpus striatum has 3 pair parts -Archistriatum, Paleostriatum and Neostriatum, these are named according to their function.
- The 3 principles regions of the cortex or Paleo-cortex, Archi-cortex and Neo-cortex.
Comparative account of telencephalon:-
Fish:-
- Cerebral consist of a primitive sensory pallium and a motor area, the globus pladius.
- The paleocortex and archicortex where thought to be related only to olfaction. It is now known that the much of the cotex in may fishes are not olfactory in function.
- The olfactory lobes are very large.
- Parafycis remains as a delicate structure.
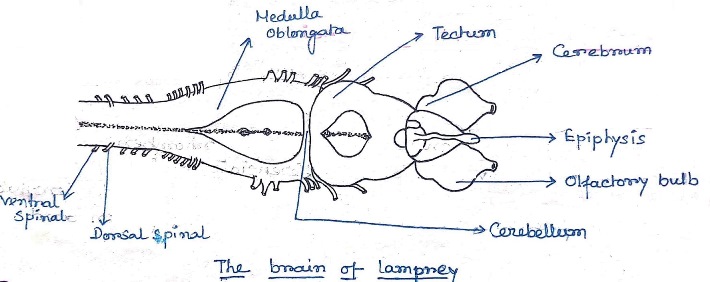
Amphibian:-
- The premitive pallium and globus pladius are still prominent in amphibians.
- Additional neuclei have invobved to participate more extensively in coordinating inloming sensory information and in directing responses to appropriate sometic masculature.
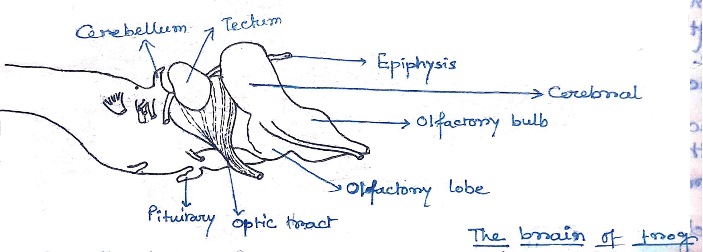
Reptiles:-
- Cerebral has become larger than those of amphibians.
- The hemispheres bulge laterally,dorsally,and backwardly over the diencephalon.
- Presence of dorsal ridge receives visual, orditory and sometic sensory stimulate.

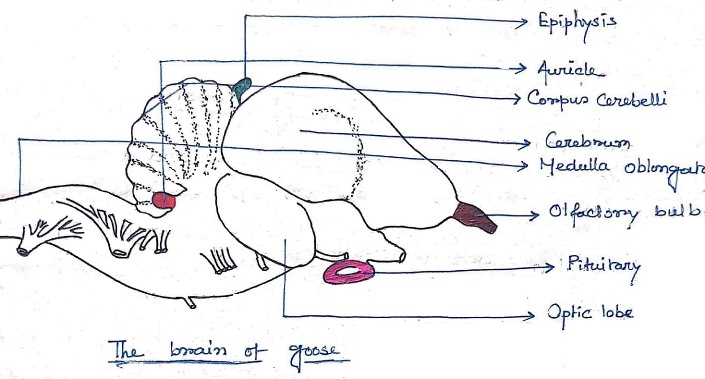
Birds:-
- birds brain is much more like reptiles.
- An additional stratum of neurons has been added capping the ridge.
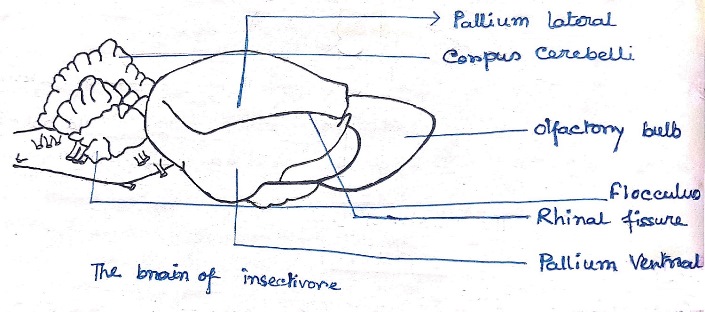
Mammals:-
- The walls and roof of the lateral ventricles has become expended in all available directions, with the formation of mammalian neocortex, the neocortex has been divided topographically into frontal, parietal, temporal and oxipetal lobes.
- In most mammals the cortex is volumines and it is folded into ridges(gyri) and grooves(sulci) that increase the working area of hemisphere.
- These folds are lacking in monotripes, marsopials, and many rodents.
- Formation of the neocortex resulted in a massive band of white matter that connects the cortex with the brainstem.
- In the roof the ventricles a broad transferase sheath of fibres, the corpus callosum is present connecting the neocortex of the two hemispheres. Corpus calotion is absent in monotrines and marsopials.
- 254 reads